Anxiety is a common and natural emotional response to stressors and challenges in life. However, when anxiety becomes chronic, excessive, or overwhelming, it can significantly impact an individual’s well-being and daily functioning. Recognizing the signs of anxiety is crucial for early intervention and effective management. In this essay, we will explore the various signs and symptoms of anxiety, shedding light on the invisible struggle that many individuals face.

Types of Anxiety Disorders
According to the American Psychological Association, an anxiety disorder is characterized as a condition where you have intrusive concerns and thoughts of a recurring nature. There are several different kinds of anxiety disorders. These disorders tend to interfere with how you process emotions. They can also cause alterations in behavior. Some anxiety disorders also involve physical symptoms. The most common anxiety disorders include:
- Generalized anxiety disorder
- Panic disorder
- Phobias
- Post-traumatic stress disorder
- Health anxiety
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
- Perinatal OCD (also known as perinatal anxiety)
- Body dysmorphic disorder

Image credits to: VERIHEAL
Body
- Physical Symptoms: Anxiety often manifests physically, affecting the body in several ways. Some common physical signs of anxiety includes: A. Rapid heartbeat and palpitations b. Shortness of breath or hyperventilation c. Muscle tension and aches d. Trembling or shaking e. Sweating excessively f. Gastrointestinal problems, such as nausea or diarrhea g. Insomnia or disrupted sleep patterns h. Fatigue and restlessness. These physical symptoms can be unsettling and contribute to the overall distress experienced by individuals with anxiety.

LAILA SAMPHILIPO / THE TEMPLE NEWS
2. Emotional Signs: Anxiety is primarily an emotional response, and its emotional signs can be equally debilitating. These signs may include: a. Excessive worry or apprehension about future events – b. Irritability and mood swings c. Feelings of dread or impending doom d. Difficulty concentrating or racing thoughts e. Exaggerated fears and phobias f. Overwhelming sense of unease or restlessness g. Panic attacks characterized by intense fear and physical symptoms. The emotional turmoil caused by anxiety can disrupt one’s personal and professional life.

3. Behavioral Signs: Anxiety often affects a person’s behavior and daily activities. Some behavioral signs of anxiety include: a. Avoidance of certain situations or places that trigger anxiety b. Social withdrawal and isolation c. Procrastination or difficulty making decisions d. Compulsive behaviors or rituals to alleviate anxiety (e.g., excessive hand washing) e. Overeating or loss of appetite f. Substance abuse as a means of self-medication g. Difficulty in initiating or maintaining relationshipsThese behavioral patterns can lead to significant impairment in an individual’s life.
4. Cognitive Signs: Anxiety can also impact one’s thoughts and cognitive processes. Cognitive signs of anxiety may include: a. Catastrophic thinking, expecting the worst-case scenario b. Perfectionism and excessive self-criticism c. Negative self-talk and self-doubt d. Racing thoughts and an inability to focus e. Obsessive rumination on past events or future concerns f. Impaired memory and forgetfulnessThese cognitive signs can interfere with problem-solving and rational decision-making.
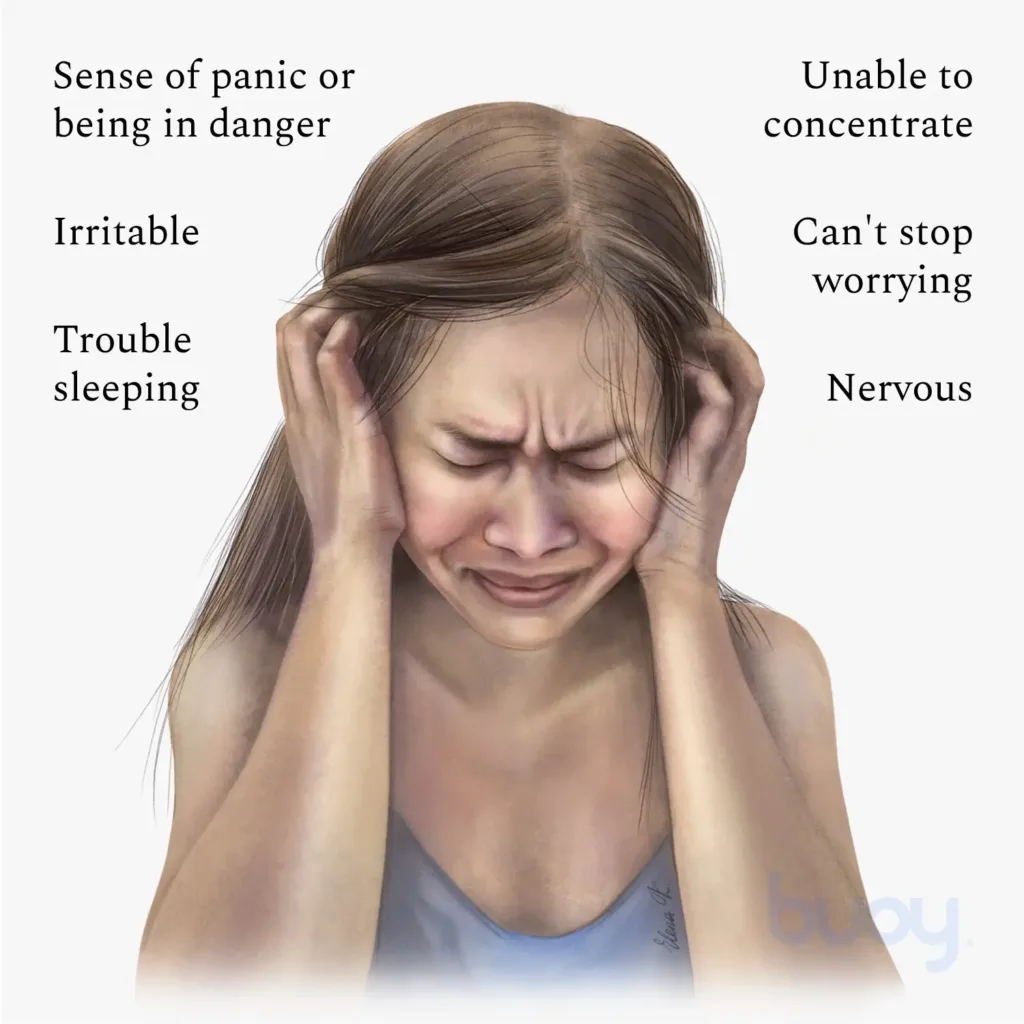
Image credits to: www.buoyhealth.com
Conclusion
Anxiety is a pervasive and often invisible struggle that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It can manifest through a range of physical, emotional, behavioral, and cognitive signs. Recognizing these signs is essential for early intervention and support. Anxiety is a treatable condition, and with the right strategies, individuals can learn to manage their symptoms effectively.

Image by: www.opencolleges.edu.au
It is crucial to promote awareness and understanding of anxiety to reduce the stigma surrounding mental health issues. Education, empathy, and support from friends, family, and healthcare professionals are essential in helping those who experience anxiety to navigate their challenges and regain control over their lives. By acknowledging the signs of anxiety, we can take the first step towards creating a more compassionate and inclusive society where individuals struggling with anxiety receive the care and understanding they deserve.
Self-Help Strategies

Image by: https://www.calmclinic.com/
There are several self-help strategies that can complement therapy:
- Keep a journal to track your thoughts and emotions.
- Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation.
- Challenge negative thoughts and replace them with more balanced and realistic ones.
- Set achievable goals and celebrate your accomplishments.


